|
Last update 08-Oct-14
|
Nice Hair! Bea Alonzo (Filipina actress)
This picture of a pretty model with beautiful shiny hair comes into mind when mentioning the word "keratin". Keratin appears to be synonymous with a magic formula for haircare products. This scientific website will distinguish between facts and fiction about keratin and its intermediate filament superfamily of proteins. The focus however is, the technological breakthroughs in materials engineering and in applications for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine, not cosmetics.
Keratin Biomaterials According to Prof. Black (author of one of our Biomedical Engineering textbook), a biomaterial is "a nonviable [non-living] material used in a medical device, intended to interact with biological systems" (Black, 1999). Since biomaterials are employed to build therapeutic clinical devices (such as an artificial pacemaker, hydrocephalus shunt, and peripheral nerve conduit, among others) that come into contact with the living biological host environment; they all must have the property called biocompatibility. Our group and other researchers have demonstrated that keratin extracts from human hair, sheep wool, chicken feathers, etc. are biologically-compatible or biocompatible. These protein preparations are hence referred to as keratin biomaterials.
Still in the process of Editing...
|
Type IK9
K10 K12 K13 K14 K15 K16 K17 K18 K19 K20 K23* K24* |
Type IIK1
K2 K3 K4 K5 K6a K6b K6c K7 K8 K76 K77 K78* K79* K80* |
*Still unknown gene expression pattern
B. Hair follicle-specific epithelial keratins
Type IK25
K26 K27 K28 |
Type IIK71
K72 K73 K74 K75 |
C. Hair keratins
Type IK31
K32 K33a K33b K34 K35 K36 K37 K38 K39 K40 |
Type IIK81
K82 K83 K84 K85 K86 |
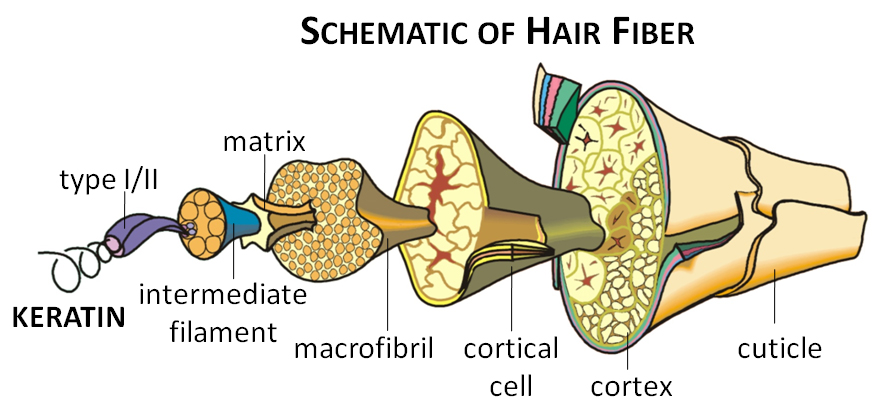
What are hair keratins?
The majority of the hair strand is composed of keratins that make up the outer protective cuticle and the inner cortical cell units. Hair keratins provide shape, strength, and integrity to the hair fiber. Keratins, in general, are fibrous structural proteins that belong to the intracellular intermediate filament (IF) superfamily. Type I (acidic) and type II (basic to neutral) IF keratins form coiled-coil obligatory heterodimers through the interaction of their α-helical rod domains. Two dimers assemble in a staggered antiparallel fashion to make a tetramer. Subsequently, two tetramers form an octamer and four octamers join together to build a cylindrical unit length filament (ULF). End-to-end linkages of ULFs and the process of compaction enable the formation of a mature 10 nm-diameter IF with multiple mechanical, biological, and signaling functions. Aside from hair keratins, other keratin group members include epithelial and hair follicle-specific epithelial keratins. Hair keratins have relatively high sulfur content in their head and tail globular domains, and are further reinforced by a continuous phase of highly cross-linked matrix proteins referred to as keratin-associated proteins (KAPs).
Keratin Biomaterials
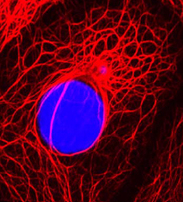
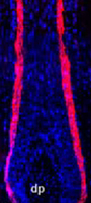
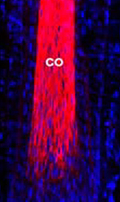
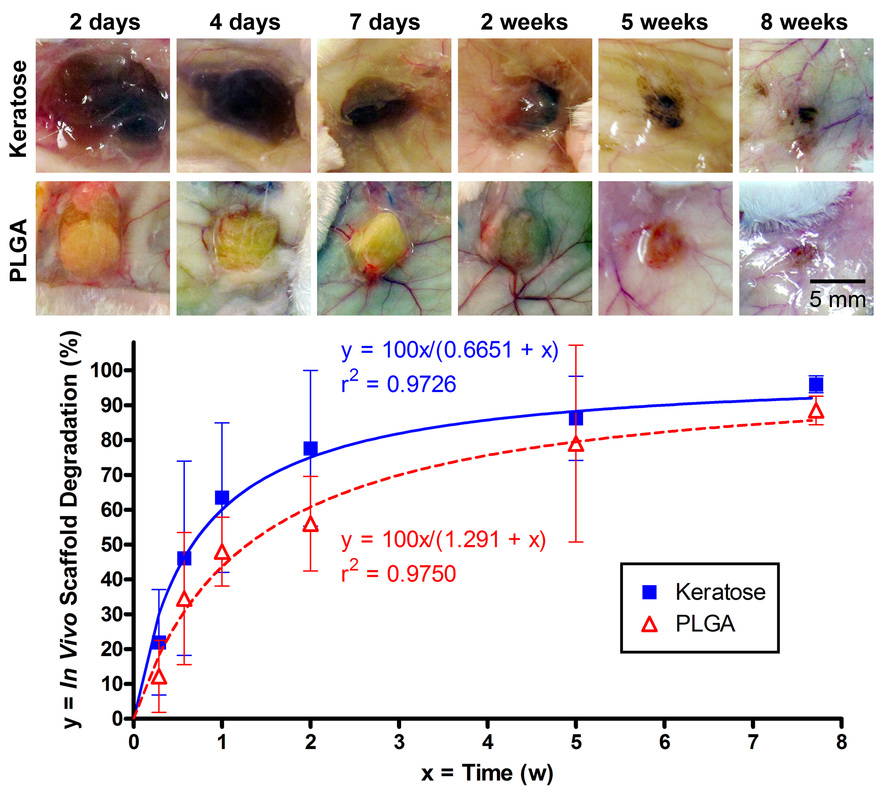
Soluble keratin extracts (keratin IF proteins and KAPs), mostly from the cortex, have been processed into biomaterials and shown not only to provide physical support structures, but also to allow for cellular attachment, proliferation, and viability, indicating the presence of ligands where cell-surface receptors can bind. Furthermore, keratins employed as temporary matrices for tissue repair and regeneration of injured peripheral nerve, spinal cord, skin, and bone have displayed promising results. Host cells were able to use the keratin network as a substrate for infiltration and formation of native structures. Overall, these studies suggest that readily-available human hair keratins have the potential to be a relevant new biomaterial platform for cell culture and tissue engineering applications.
Please post your msg here :)
HTML Comment Box is loading comments...